USING GIT
My first step in understanding git was to visit the useful tutorials on the Fab Academy site. You can find them HERE. For the sake of understanding it better I will describe it as simply as possible.
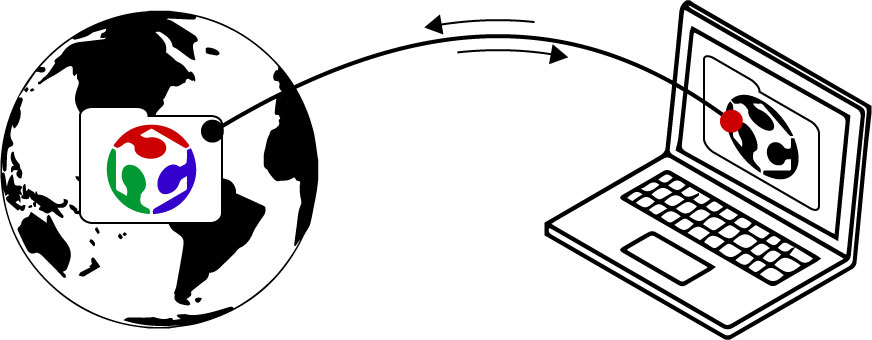
WHAT IS GIT?
USEFUL LINKS:
Fiore Basile Tutorial
git-scm.com
try.github.io
Git Cheatsheet
Fab Academy Tutorials
Git is a version control system. Version control is a useful solution to keep track of changes made to documents, folders, and kernals of information that are stored on a server or computer. This makes it possible to review changes, avoid mixing up files, and track a history of updates made to your work so that your process can be revisited and reviewed by others. This is especially important if a group of people are sharing information. As is the case for the Fab Academy, or when developers are working on open source software, for example.
This way, people can learn from your projects and, if permitted, make suggestions or changes to your work which you can re-incorporate. Without version control, it would be significantly harder to develop open source tools.
GitLab is the version control tool chosen by the Fab Academy to keep track of all of the useful information we generate through our work. It can track changes we make to our websites by establising a link between a folder on your computer and a repository, or "repo" which is located on a Fab Academy server. This repo generates the necessary metadata required to keep track of our collective work and makes it searchable to others. When you update your website in that folder, you are expected to push it onto the repo which will mirror exactly what is on your computer. The opposit is also true. If someone shares or changes a file on the repo, you can pull this onto your computer. At any given time, your local folder should be identical to the folder located on the repo.
GitLab is one implementation of Git. There is also GitHub and other flavors. To understand the differences between GitLab and GitHub click HERE. As Fab Academy students, GitLab is also acting as an ecosystem and host for the entire Fab Academy infrastructure including our individual pages. It also allows users to communicate, share ideas, and report issues.
CONNECTING TO GITLAB
Note:We are encouraged to use our computer's Terminal as a way to quickly access programs and files. Although you can work directly from the GitLab interface, there is more to learn through Terminal's text-based process and it arguably provides quicker access when you know how use it properly.
STEP 1:
Generating an SSH key.
---> Generating an SSH key is necessary so that GitLab can identify your computer and make a secure connection to your local folder.
Following the help examples on git.fabacademy.org I executed the following commands but replaced email@example.com with my personal email.
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub | clipDone properly, you should get a response like this:
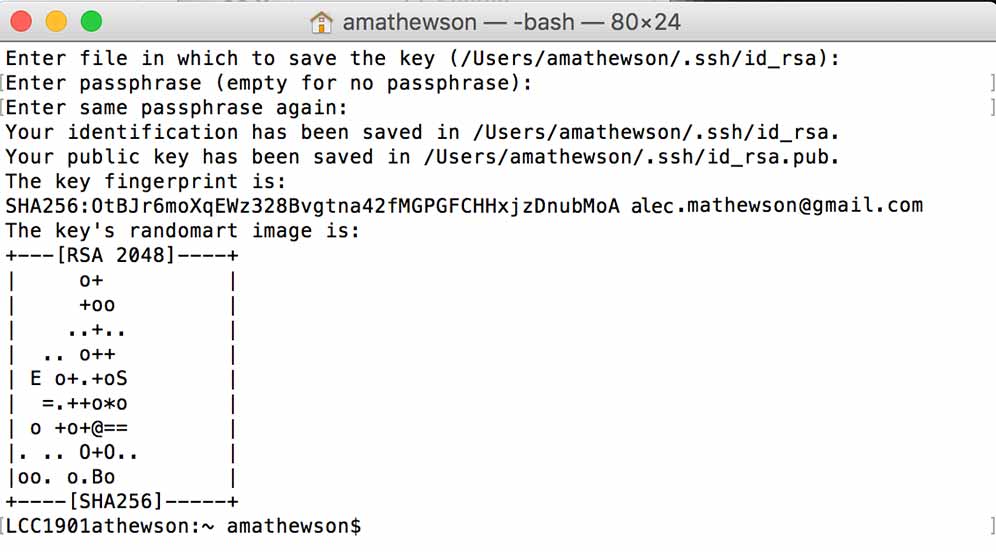
Note:This was my first SSH key and I also opted for all the default settings. When prompted to enter a file to save the key and a passphrase I left it blank.
STEP 2:
Copying your public SSH Key and putting it on GitLab
---> If you want to see your public SSH key enter
[cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub] in your terminal but you can also copy it directly to your clipboard by entering the following command.
pbcopy < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub---> With your public key now in your clipboard, go to th GitLab and pull down the settings tab under your user icon.
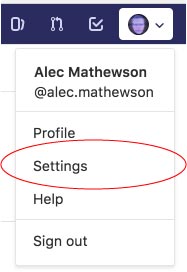
---> Navigate to the SSH section in your settings.
---> "Command V" / paste your SSH key in the designated section.
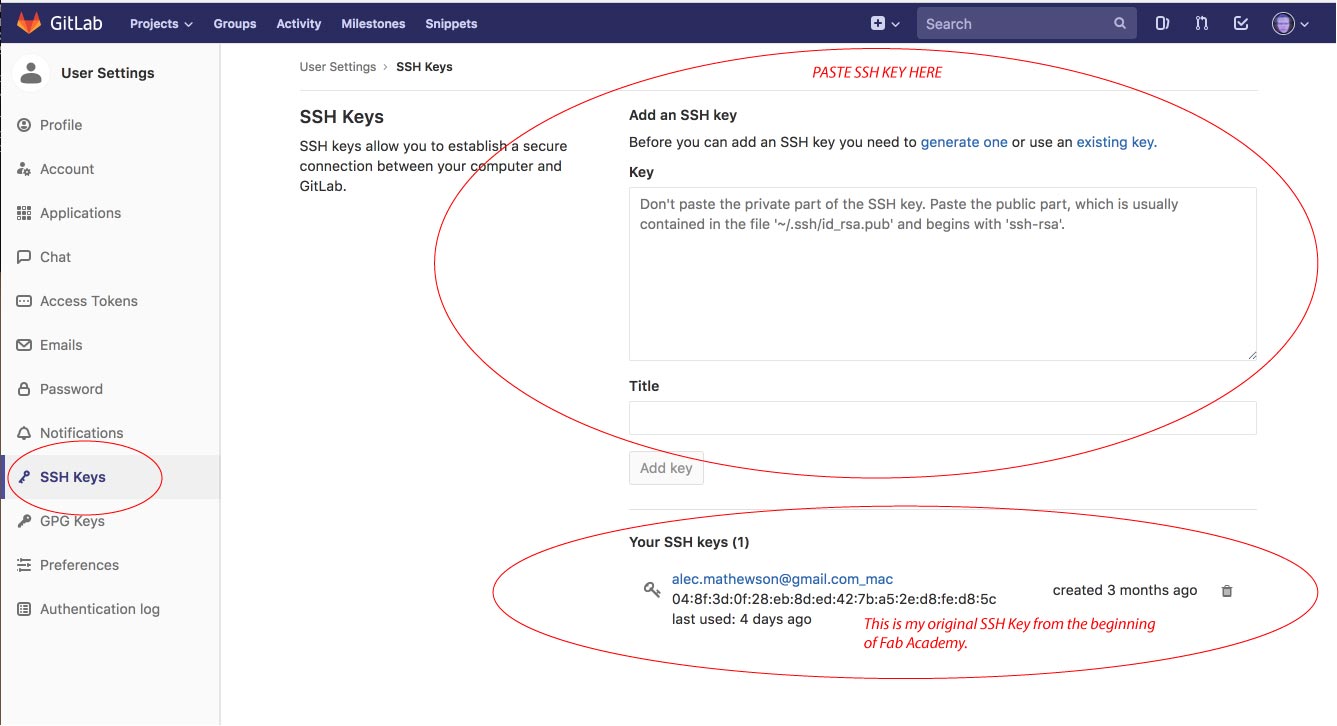
Note: I did not get a proper screen capture the moment I did this step. My SSH key was generated at the beginning of the Fab Academy so you will notice it here at the bottom of the above window. This screen shot was taken 3 months later
STEP 3:
Publishing Your Website
In order to publish your website. You need to create a gitlab-ci.yml file. What is this? The gitlab-ci.yml file lives in the root of your repository. Its purpose is to configure service called CI(Continuous Integration) which basically helps build, test, and deploy, your website. It will automatically update your webpages when you commit any changes through git. To finalize this step you need to generate your .yml file by following these steps on your GitLab portal page:
---> Navigate to the root of your repository and select "New File"from the dropdown menu next to your username.
Note: You will notice in the image above that my root is already populated and that there is already a gitlab-ci.yml in there. This is because I had to created the documentation for this step after my site had already been published. Normally, this folder would be empty.
---> Choose a template type by selecting "gitlab-ci.yml" in the dropdown menu.
---> Apply an HTML template to the gitlab-ci.yml file.
---> Completed, it should look like this:
USING GIT
Using Git took a bit of time for me to get used to. Before mucking up any website attempts I first attempted sharing some test files until I understood the right process. I was unsuccessful at first but it turns out I was not in the right directory. Once I navidated to the master folder on my computer, "alec-mathewson" using the cd command I was able to successfully copy a test document.
Here is a list of commands to make this happen
cd ---> Change directory. Use this to navigate within different directories in your computer.
cd Documents/FabAcademy/alec-mathewsonls ---> Look up file. Use this to see what files are in your current directory.
git add ---> Add files you wish to sync with the repo. You can add specific files or all files.
"git add ." == stage new and modified files.
"git -A" == stage all files / new, modified, and deleted files.
"git add -u" == stage modified and deleted files.
git commit ---> Stores / commits the new changes made to the index. It basically stores all the changes and keeps them logged and ready to be officially pushed to the repo. You are expected to add notes to your commits otherwise it won't work. git commit -m includes the message. Looks something like this:
git commit -m "added notes to the git section of week2"git status ---> Verify all the changes you have logged before pushing them to the repo. It is good practice to verify what you are pushing onto the git repo and check for errors before you do it.
git push ---> Finalize the process by pushing your commits or changes to the repo.
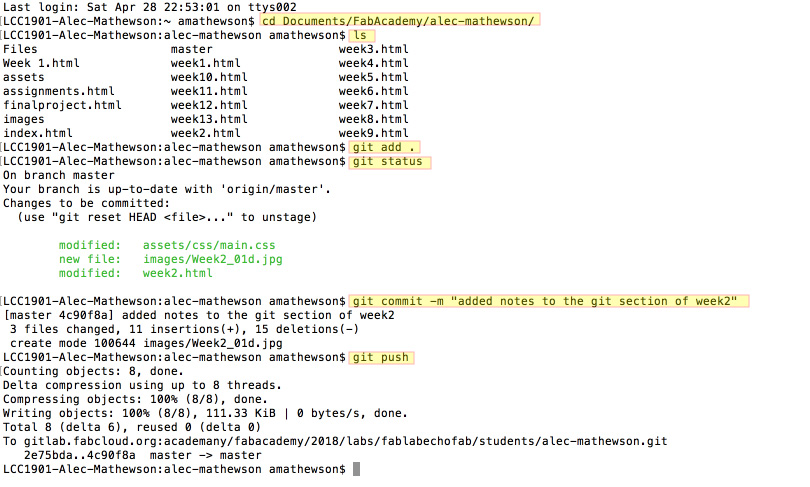
There are a lot more elements to using Git and many more specific commands but with these few elements you are able to keep your website updated and your folders in sync.