Back To Top
Week 12 - Molding and casting
Measuring the material needed
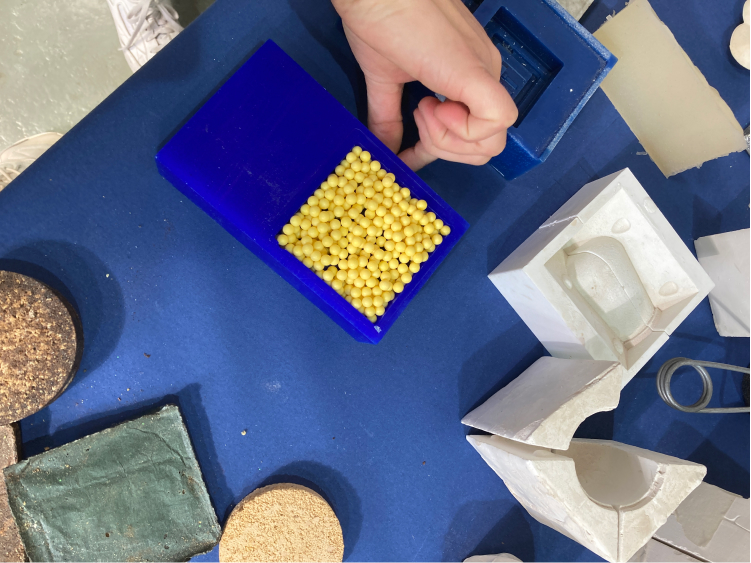
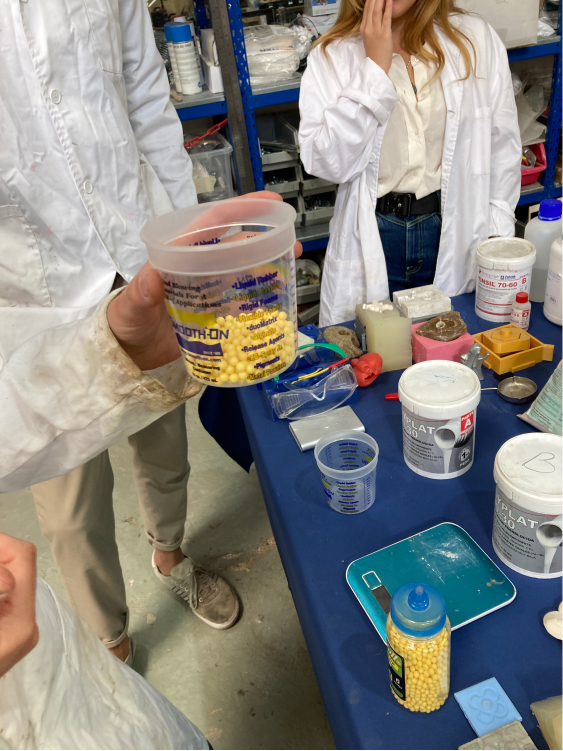


Before we do our mold we need to measure how much material we will need to fill it in. We don't want to waste material but also we don't want to be short. We can measure the space using a specific product which is bubbles of rubber. In our case, the ones we have at the lab are quite big and not very good for detailed and small molds.
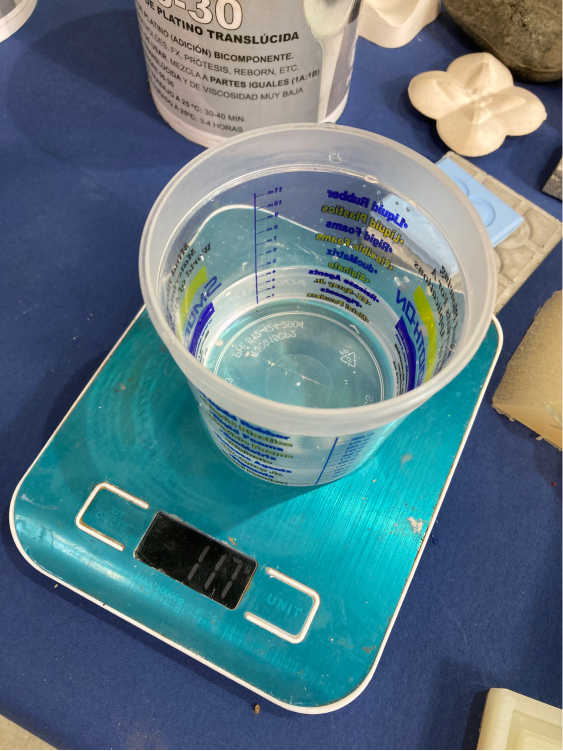


Luckily we can also measure with water, simply by filling in the mold with water and then using this water to know how much material we would need. Using a precision scale we can also remove the weight of the cup so that we are more precise when measuring the material.
Molding with silicone
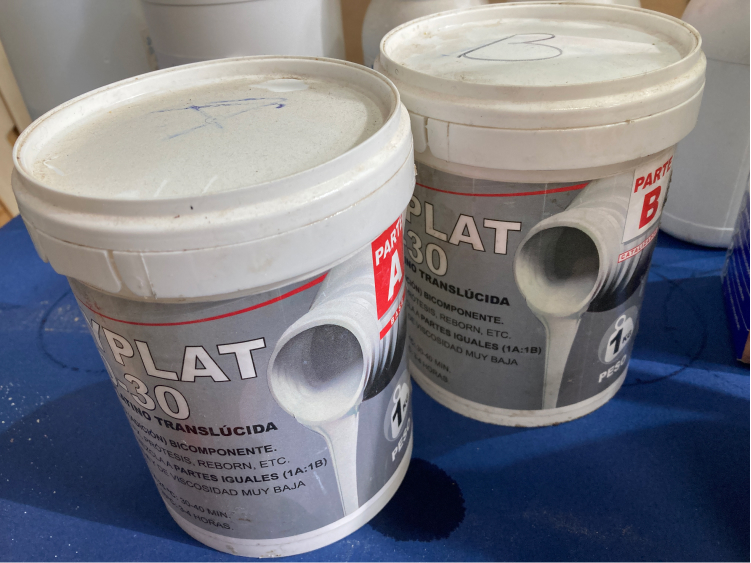

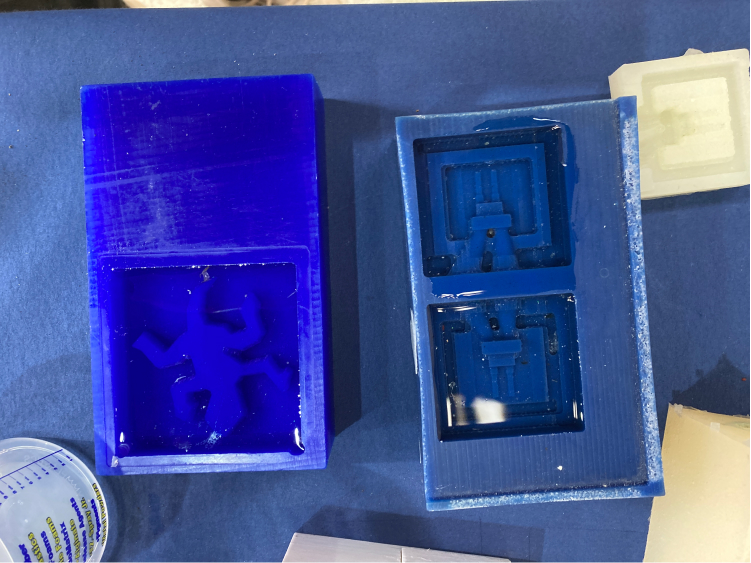
At FabLab Barcelona we have a few types of silicone, the one here in the picture is called Easy Plat 00-30, by Feroca and it is platinum silicone, specific for molding. The working time is between 30-40m (after that the chemical reaction is not going to work anymore) and it will dry in about 3-4h.

Before we pour the silicone mix we need to make sure there is no water so that the silicone can reach all the corners of the mold.
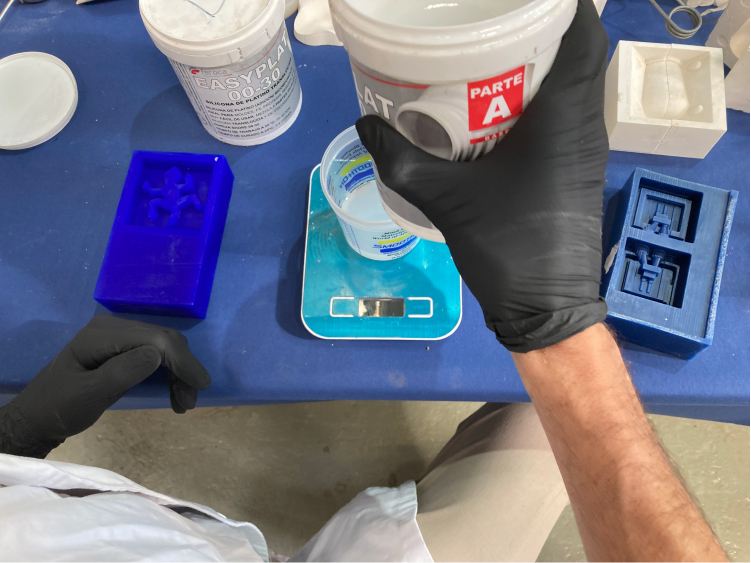
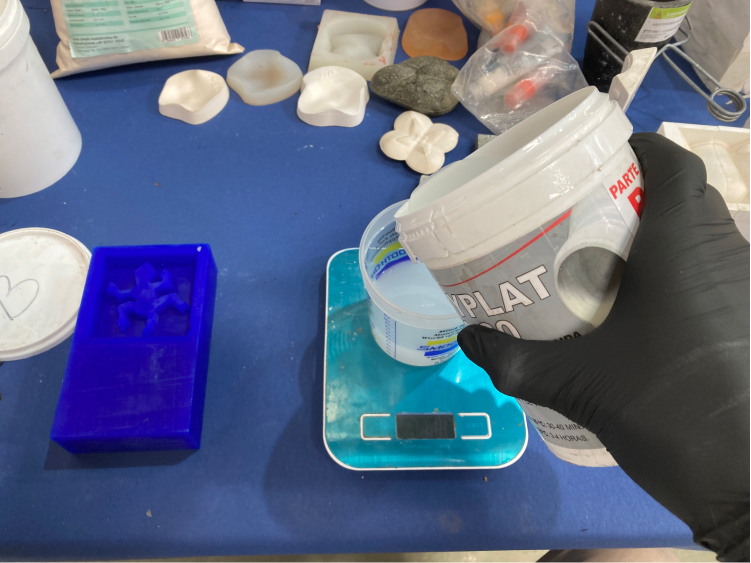
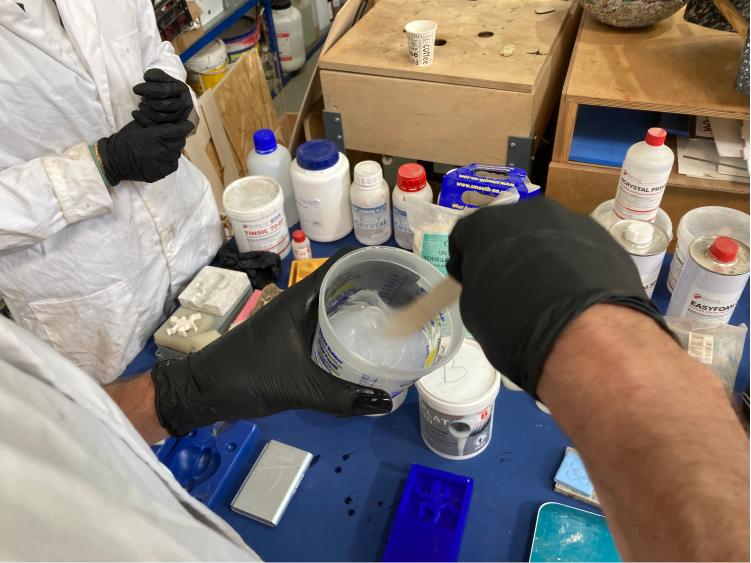



To make the mix with this material is very easy (as the name says) there are 2 parts, A and B, and they should be mixed in equal parts. So we take the total measurement of the water and divide it by 2 (excluding the weight of the cup). Then we just need to mix it for about 6m, and then mix another 5m just to make sure it is really consistent.

It is very normal de air to get trapped inside the silicone, this creates bubbles of air, we can just beat the cup on the table to make the bubbles come out or we can us a vacuum chamber as we have in the lab. The vacuum chamber puts pressure into a closed recipient making the bubbles come out faster.
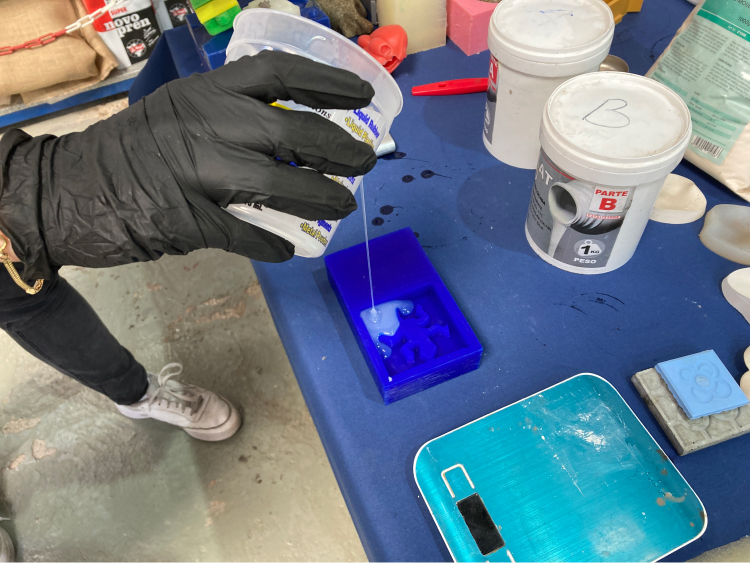

Once it is ready we need to carefully pour the silicone mix into the mold, always in the same position and dropping a very thin line.
Biomaterials
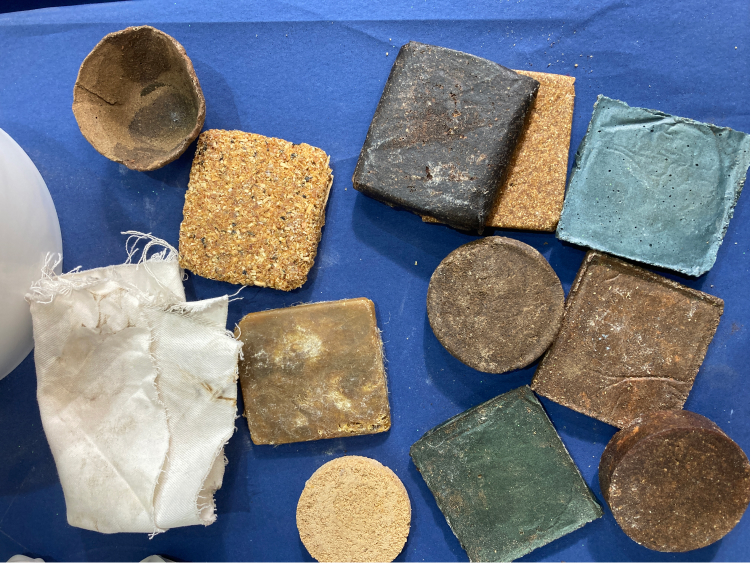

We can use also to creates mods biomaterial, without the need to have plastic and using our biological waste, such as food scraps. This promotes an alternative perspective, one that advocates for a circular society. We can explore previously discarded materials from these linear systems and creating innovative products, platforms, and processes.
For example, one recipe that we saw in class is making biomaterial out of pine resin and food waste, for this, we need vessels, sieve, syringe, scale, baking paper, spoon, silicon spatulas, mold, a pot to cook and a stove. Then, 45g of pine resin, 100g of dehydrated food scraps such as orange peel, carrot or yerba mate, then 5g of carnauba wax and 20ml of alcohol 96º.
More mold types
It is possible to use various types of molds, depending on the purpose, material, and other conditions.
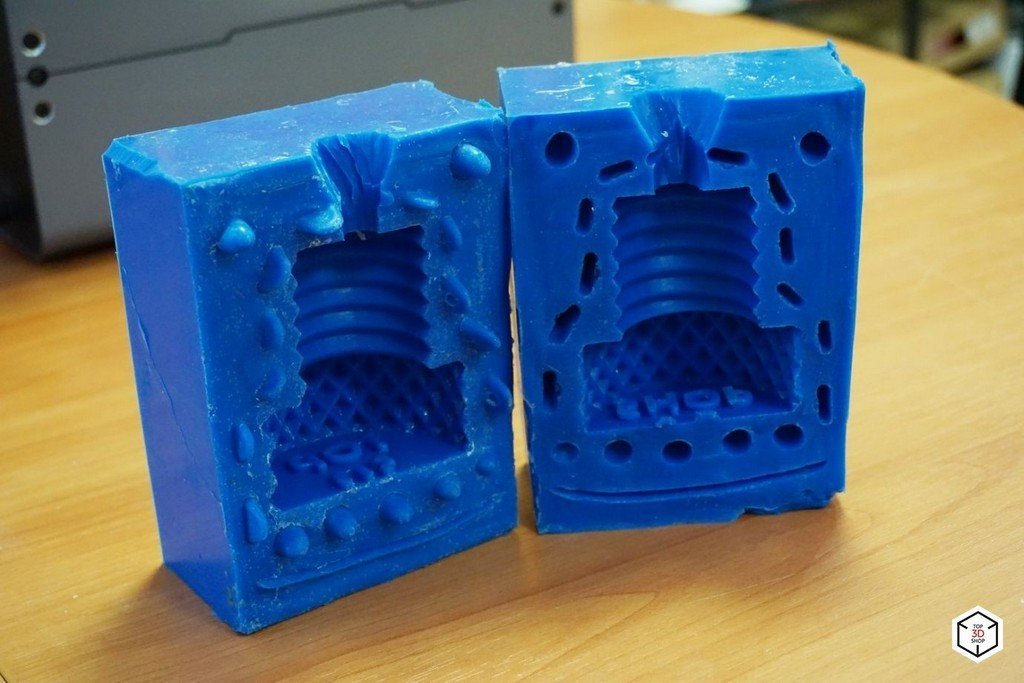
- The two-piece pattern is used for complex casting. This type of pattern has separation planes, which may have a flat or uneven surface, and the exact position of the plane is determined by the shape of the casting. The pieces need dowel, matching recesses on one half and protrusions on the other half, to align the two halves of the template detachable part.
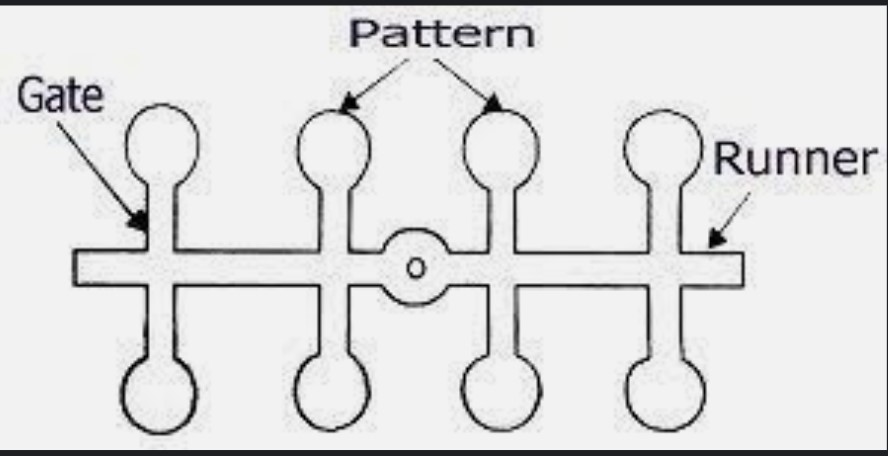
- A gate template can be composed of one or more templates into a molding template. It is designed for a mold that produces multiple components in a single casting process. Gates are used to combine different patterns, while chutes are used to create a flow of materials.